A condition of the lungs characterized by overdistension of air spaces distal to the terminal bronchioles arising from dilatation or destruction of their walls.
Causation / Etiology
The main cause is smoking
Age
Air pollution
Recurrent Upper and Lower Respiratory Tract Infection
Chemical fumes and dust in the industrial belt
Chronic bronchitis
Untreated pneumonia or latent pneumonia
Symptoms
Exertional dyspnea
Cough and sputum may develop after breathlessness
Considerable loss of weight and weakness
Wheezing sounds
Signs
General
The patient is thin with an anxious expression
Decrease in the length of windpipe substantial over the sternal notch
Tracheal descent with inspiration
Contraction of sternomastoid and scalene muscle on inspiration
Excavation of supraclavicular and suprasternal fossae on inspiration
Jugular venous filling during expiration
Indrawing of costal margin during inspirations
Cyanosis is present
On examination of the chest
Barrel-shaped chest (A/P diameter increased)
Movement diminished
Vocal fremitus diminished
Percussion note normal or hyper resonant
Breath sounds diminished, vesicular with prolonged expiration
Vocal resonance normal or reduced
Rhonchi and coarse crepitation due to associated bronchitis and associated bronchospasm and infections.
Investigation
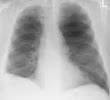
X-ray: Unusually translucent lung field with the loss of peripheral vascular markings
Bullae
A low flat diaphragm, which moves poorly on fluoroscopy
The unusual unmistakable quality of the pneumonic blood vessel shadows at the hila
In later stages with RVF, there is an enlargement of the main pulmonary artery, right ventricle, and atrium, later on, all cardiac chambers.
Pulmonary functions test:
Forced expiratory volume in one second is reduced
Forced vital capacity is also sun-normal.
Complication
Respiratory failure
Sec. polycythemia
Pul. Hypertension
Right ventricular failure (chronic corpulmonale)
Pulmonary hypertension.
Treatment
No Smoking, reduction in atmospheric pollution
Prompt treatment of acute respiratory infection
Surgeries for COPD
Bullectomy- the large emphysematous bullae are removed via CO2 laser
Reduction pneumoplasty- bilateral resection of lung volume 20-30%
Lung transplantation
Obesity must be corrected.
Differential diagnosis
Chronic bronchitis, Left-sided cardiac failure
Spontaneous pneumothorax
Giant bullae
Bronchial carcinoma
Pneumoconiosis
Pulmonary tuberculosis
Is Emphysema Cancer?
Cellular breakdown in the lungs is among the most well-known diseases around the world. In the United States and other industrialized nations, it's the significant reason for malignancy mortality.
Emphysema is a term that portrays primary changes in the lung related to constant obstacle aspiratory infection (COPD)‚ yet it's not malignancy.
The two lung sicknesses share significant danger factors basically because of the openness of tobacco smoke. COPD is a realized huge danger factor for lung malignant growth, while cellular breakdown in the lungs has been connected to changes in lung work normal for emphysema. How about we survey the connection between both emphysema and cellular breakdown in the lungs
Emphysema is an ongoing lung infection that falls under the umbrella of COPD. There are two fundamental sorts of COPD — ongoing bronchitis and emphysema.
Ongoing bronchitis happens when your aviation routes become bothered and excited, bringing about the development of bodily fluid and hindrances.
Emphysema is a condition where the small air sacs (alveoli) in your lungs, which grow and contract with every breath, lose versatility.
The alveoli lose their capacity to contract after development, and air stays caught inside. Over the long haul, this can make irreversible harm to the alveoli.
Alveoli is the place where oxygen is moved to your blood. So when there are fewer alveoli working, less oxygen gets to your blood.
While the two conditions are connected to smoking, the maturing interaction additionally brings about a decrease of lung work like that of somebody with emphysema. As we age, three things occur: Alveoli can lose their shape and become excessively agreeable; the stomach — the principal respiratory muscle — becomes more vulnerable, diminishing the capacity to breathe in and breathe out; and nerves in aviation routes become less touchy to unfamiliar particles. At the point when particles develop in the lungs, they can harm the lung tissue. These progressions can bring about indications like exhaustion, sluggishness, and windedness.
Cellular breakdown in the lungs in itself isn't COPD. Cellular breakdown in the lungs happens when unusual lung cells increase and group out the cells that regularly help tissues and organs to work.
Sometimes, cellular breakdowns in the lungs can be auxiliary or spread to the lung from another area. Be that as it may, 90% of cellular breakdowns in the lungs are connected to cigarette smoking.
While smoking cigarettes can straightforwardly harm your lungs, breathing recycled smoke can likewise harm the lungs. Different poisons can likewise do this, including breathed in synthetic substances and other natural contaminations.
When these cells are harmed — from conditions like COPD — they are more inclined to get unusual, or destructive.
While emphysema and cellular breakdown in the lungs are two distinct conditions, they do share a few affiliations and offer the fundamental danger factor for both which is cigarette smoking. Both can prompt resistant framework glitch, irritation, and cell harm which assume a part in the advancement of the two sicknesses.
While the physiology of emphysema itself doesn't cause a cellular breakdown in the lungs or the other way around, either condition may establish a climate wherein the other can flourish. For instance, cell harm from emphysema can cause pressure and hereditary changes in the lung tissue. In like manner, malignant growth cells can harm alveoli and other lung tissues, bringing about COPD-like conditions.
Indeed, one investigation proposes that emphysema is the most grounded known marker for the advancement of cellular breakdown in the lungs. It is not necessarily the case that emphysema is a cellular breakdown in the lungs, just that individuals with emphysema are at a higher danger of in the long run creating a cellular breakdown in the lungs.
The side effects of emphysema and cellular breakdown in the lungs are comparative solely, however not all.
The accompanying side effects, then again, are more normal in individuals with a cellular breakdown in the lungs — in spite of the fact that they may likewise happen in serious emphysema or during COPD intensifications:
A specialist may assess you for COPD or potentially screen you for the cellular breakdown in the lungs in case you're in high danger of one or the other condition because of smoking, working environment openness, or different variables.
You might be alluded to a subject matter expert, similar to a pulmonologist or oncologist, to track down the best medicines. Early analysis and treatment are critical for the two sicknesses.
At the point when it's a crisis
Windedness and other breathing issues are viewed as a crisis in the event that you:
Cellular breakdown in the lungs and emphysema are two altogether different conditions, yet they have comparative danger components, causes, and side effects. Both can be brought about by cigarette smoking or other harm to lung tissues.
On the off chance that you experience difficulty breathing, or a persistent hack that is deteriorating, see a medical services proficient.
Homeopathic medicines (Expert Homeopathy: Dr. Anutosh Chakraborty)
Ammonium Carb: It is very good medicine for emphysema, for old aged debilitated persons.
Antim Tart: Emphysema of the aged, coughing and gasping consecutively.
Ipecac: Dyspnea, constant constriction of chest. Hack cough unending and violent with each breath.
[Homeopathy believes in Constitutional treatment]

Post a Comment